
Robotics in manufacturing involves deploying programmable robotic systems to automate tasks that are repetitive, labor-intensive, or hazardous. These robotic systems are designed to operate continuously while maintaining consistent quality, accuracy, and throughput.
In many manufacturing environments, robotics is introduced to stabilize processes that are difficult to staff, prone to variation, or limited by manual cycle times. Robots excel in applications where consistent motion, predictable outcomes, and high uptime are critical to overall production performance.
Manufacturing robots are commonly integrated with PLC systems, SCADA platforms, HMIs, and industrial networks to provide centralized control, monitoring, diagnostics, and data collection across the production environment.
Industrial robots are used across a wide range of manufacturing applications, including:
Robotics automation improves consistency, reduces cycle times, and supports higher production volumes. In many cases, robotic systems also enable manufacturers to redesign workflows, reduce work-in-process inventory, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Different manufacturing applications require different robot designs and capabilities:
Selecting the right robot depends on payload requirements, reach, speed, accuracy, duty cycle, and application complexity. Environmental conditions, part variation, and future production requirements are also important considerations during system design.
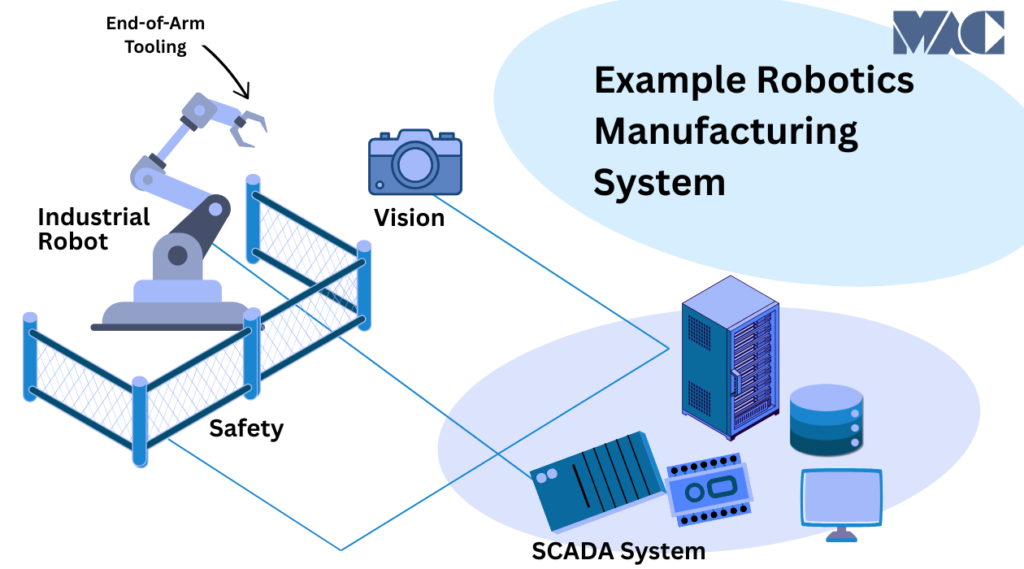
The robot provides the mechanical motion and control required to perform the task.
Controllers manage robot motion, sequencing, safety logic, and communication with PLCs and other automation systems.
Custom grippers, weld guns, vacuum tooling, or process-specific tools allow the robot to interact with parts and equipment.
Vision systems and sensors provide real-time feedback for part location, orientation, inspection, and error detection.
Safety-rated controllers, fencing, scanners, and light curtains help ensure compliance with industrial safety standards.
Manufacturers implement robotics solutions to achieve significant operational benefits:
Robotics automation also supports lean manufacturing initiatives, workforce optimization, and long-term production consistency. By reducing process variability and manual intervention, robotics helps manufacturers achieve more predictable and stable outcomes.
Modern robotics systems are increasingly connected to SCADA systems, PLC architectures, MES platforms, and IIoT technologies. This integration enables:
Robotics serves as a foundational technology within smart manufacturing and digital transformation initiatives.
Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of connected technologies, data analytics, and automation to create more intelligent and responsive manufacturing environments. Within this framework, robotics plays a key role by acting as both a source of production data and an execution layer for automated decision-making.
When integrated with PLCs, SCADA systems, MES platforms, and IIoT infrastructure, robotic systems provide real-time visibility into production status, cycle times, faults, and quality metrics. This data can be used to optimize processes, improve asset utilization, and support predictive maintenance strategies.
In Industry 4.0–driven manufacturing environments, robotics enables:
Robotics integration within an Industry 4.0 strategy helps manufacturers move beyond isolated automation toward fully connected, information-driven operations.
Successful robotics projects require careful planning and system design, including:
Working with an experienced industrial automation partner helps ensure reliable performance, proper system integration, and long-term value. Effective planning and commissioning reduce startup risk and help ensure that robotics systems meet both current and future operational requirements.
Robotics solutions are most effective when tailored to the specific needs of each manufacturing operation. Proper system design, integration, and support are essential to achieving consistent performance and operational efficiency.
Manufacturing robotics can be implemented as standalone systems or as part of a fully integrated automation strategy.
Robotics continues to transform manufacturing by improving efficiency, quality, and operational resilience. As automation technologies evolve, robotics remains a key driver of competitive advantage for manufacturers across industries.
Robotics is widely used across many manufacturing industries, including automotive, food and beverage, metals, plastics, consumer goods, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and packaging. Any operation with repetitive, high-volume, or tolerance-sensitive processes can benefit from manufacturing robotics.
A process is typically a good candidate for robotics when it involves repetitive motion, consistent part presentation, ergonomic risk, or production bottlenecks. Feasibility studies often evaluate cycle time stability, part variation, safety considerations, and return on investment before selecting robotics as a solution.
Robots are commonly used for tasks such as material handling, assembly, welding, painting, inspection, machine tending, and packaging. These tasks benefit from the speed, consistency, and reliability that robotic automation provides.
Robots are commonly used for tasks such as material handling, assembly, welding, painting, inspection, machine tending, and packaging. These tasks benefit from the speed, consistency, and reliability that robotic automation provides.
Manufacturing robotics systems are typically integrated with existing equipment using PLCs, industrial networks, and SCADA or HMI systems. Proper integration allows robotic systems to operate as part of a coordinated production process rather than as standalone machines.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed with built-in safety features that allow them to operate alongside human workers in certain applications. Safety requirements depend on the specific task, risk assessment, and applicable standards, and may still require additional safeguards.
Robotics integration can improve productivity, product quality, workplace safety, and operational consistency. It can also help manufacturers address labor shortages, reduce downtime, and support scalable growth.
Robotics often shifts workforce roles rather than replacing them entirely. Operators may transition to responsibilities such as system oversight, troubleshooting, quality monitoring, and maintenance. When combined with training, robotics can help improve job safety and support long-term workforce sustainability.
Implementation timelines vary based on application complexity, system size, and integration requirements. Smaller robotic cells may be deployed relatively quickly, while fully integrated automation systems require more detailed design, testing, and commissioning.
Implementation timelines vary based on application complexity, system size, and integration requirements. Smaller robotic cells may be deployed relatively quickly, while fully integrated automation systems require more detailed design, testing, and commissioning.
Yes. Well-designed robotics systems are highly scalable and can be expanded, reprogrammed, or integrated with additional automation technologies as production requirements evolve.
Common challenges include space constraints, legacy equipment integration, part variation, change management, and production downtime during installation. Addressing these challenges early through proper planning and simulation helps ensure successful deployment.
Let us help you supercharge your operations.
 MAC Automation
MAC Automation
MAC Automation is a premier provider of engineering and automation solutions, with a focus on SCADA, IIoT and industry 4.0. MAC Automation serves high-performance industries including energy, oil & gas, manufacturing, petrochemical, wastewater, research & development, and food processing.
 MAC Engineering
MAC Engineering
MAC Automation’s affiliate, MAC Engineering, provides a full-service engineering backbench to compliment MAC Automation’s offerings. MAC Engineering is a multidisciplinary engineering firm headquartered in Calgary, Alberta.
Contents
×